The universe is a vast and mysterious place, filled with cosmic forces that shape the movement of galaxies. One of the most intriguing of these forces is the Great Attractor, an unseen gravitational anomaly pulling our Milky Way and countless other galaxies toward it at astonishing speeds. But what is the Great Attractor, and what does it tell us about the large-scale structure of the universe? Join us on spaceyv.com as we explore this cosmic mystery in greater depth than ever before.
Understanding the Great Attractor
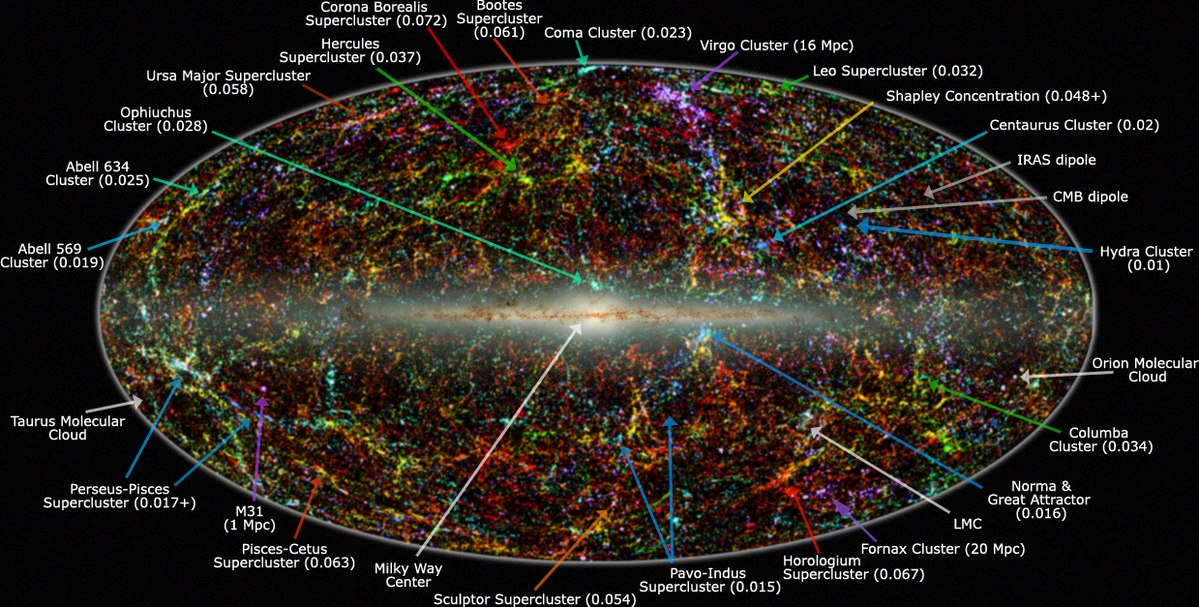
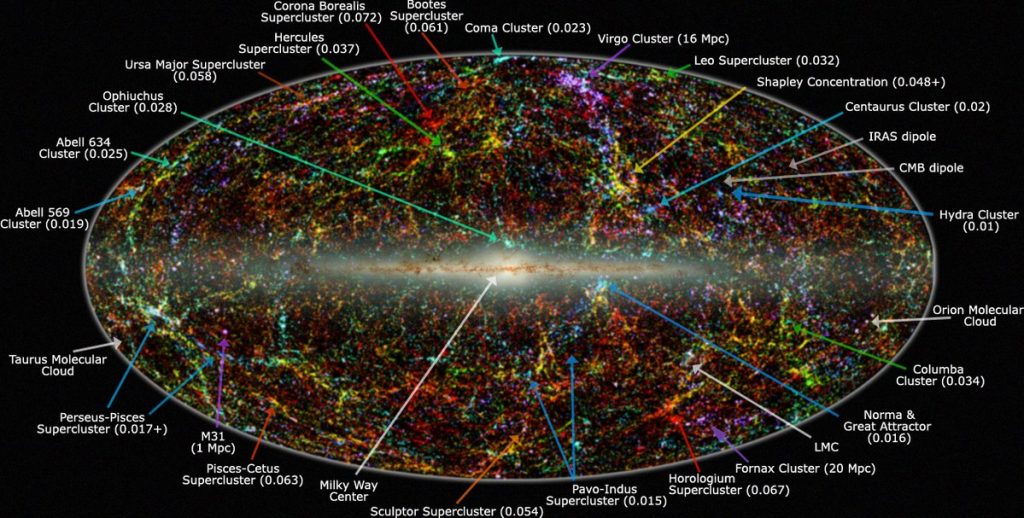
Astronomers have long known that the Milky Way, along with the entire Local Group of galaxies, is moving at a speed of over 600 km/s (1.3 million mph) toward a particular region of space. This puzzling motion suggests that there is something incredibly massive exerting an enormous gravitational pull—this unseen force is what we call the Great Attractor.
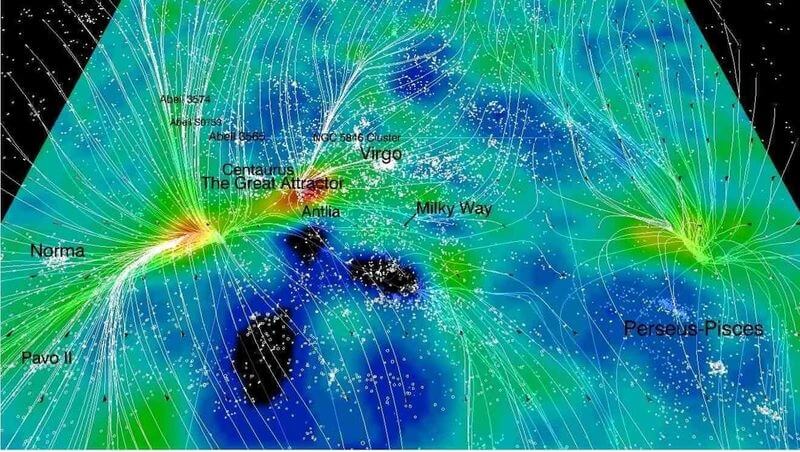
The Great Attractor is located roughly 150-250 million light-years away in the direction of the Centaurus, Hydra, and Norma constellations. However, what makes it difficult to study is that it lies in the Zone of Avoidance, the region of space obscured by the dense stars and dust of the Milky Way. This makes direct observation challenging, but its influence on the movement of galaxies is undeniable.
What Causes the Great Attractor’s Pull?
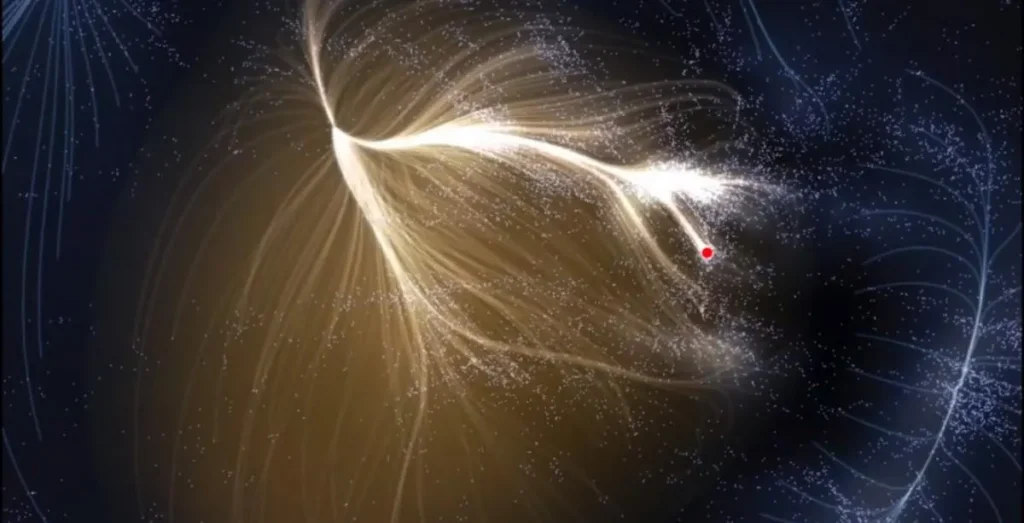
Unlike a typical celestial body such as a black hole or a supermassive star, the Great Attractor is not a single object but rather a gravitational anomaly. It represents a huge concentration of mass, including entire clusters of galaxies, dark matter, and other cosmic structures, that create a strong gravitational field.
Key Contributors to the Great Attractor’s Mass:
- The Norma Cluster (Abell 3627): A massive cluster of galaxies that lies near the center of the Great Attractor’s influence.
- The Hydra-Centaurus Supercluster: A dense region of galaxies leading toward the Great Attractor.
- Dark Matter: The mysterious invisible substance that makes up about 85% of the universe’s mass and contributes significantly to the gravitational pull.
- Luminous Matter: Although the majority of mass in the Great Attractor is likely dark matter, there are also trillions of stars, interstellar gas, and cosmic dust adding to its immense gravitational influence.
These massive structures collectively warp the motion of galaxies across hundreds of millions of light-years, affecting not just our Local Group but even distant clusters of galaxies.
How Do We Detect the Great Attractor?
Since much of the Great Attractor’s influence is hidden by the Milky Way, astronomers have had to rely on indirect methods to study it:
- Galactic Motion Measurements: By tracking the velocities of galaxies in our cosmic neighborhood, scientists have determined that they are all being pulled toward a common point.
- X-ray Observations: Telescopes such as NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory detect hot gas in massive galaxy clusters, revealing hidden structures behind the Milky Way.
- Infrared Surveys: Instruments like the Two Micron All-Sky Survey (2MASS) can see through dust and detect galaxies within the Zone of Avoidance.
- Gravitational Lensing Studies: By examining how the light from distant galaxies is bent by gravitational fields, researchers can map unseen mass distributions, including those of the Great Attractor.
With these methods, scientists have mapped out the large-scale cosmic structure and confirmed that the Great Attractor is a real and influential force in our universe.
Is the Great Attractor the Biggest Structure in the Universe?
While the Great Attractor is an important feature of the cosmic landscape, later discoveries have revealed that it is part of an even larger structure called Laniakea—a supercluster of galaxies that includes our own Milky Way.
Laniakea, meaning “immense heaven” in Hawaiian, spans over 520 million light-years and contains more than 100,000 galaxies. The Great Attractor sits within this structure, serving as one of its central gravitational nodes.
Beyond Laniakea, even more immense cosmic structures have been discovered, such as the Sloan Great Wall and the Shapley Supercluster, showing that the universe is an interconnected web of galaxies and gravitational forces. These structures highlight that the Great Attractor is not an isolated anomaly, but rather part of a much larger cosmic dance of matter and gravity.
What Does This Mean for Our Galaxy?
The gravitational pull of the Great Attractor suggests that the Milky Way is not simply drifting through space at random but is being guided along cosmic highways formed by massive galaxy clusters and dark matter. Over billions of years, our galaxy will continue moving toward denser regions of space, eventually merging with other galaxies in a grand cosmic dance.
However, the expansion of the universe caused by dark energy may counteract this motion. If dark energy continues to accelerate the expansion of the universe, the gravitational attraction of structures like the Great Attractor may weaken over time, preventing large-scale mergers from occurring as expected. Scientists continue to debate how these opposing forces—gravity and dark energy—will shape the future of our cosmic environment.
Final Thoughts: The Ever-Moving Universe
The Great Attractor remains one of the most fascinating cosmic mysteries, revealing how galaxies and structures in the universe interact on enormous scales. While we may never see it directly, its presence is undeniable, influencing the fate of our galaxy and beyond. Ongoing advancements in observational technology will continue to refine our understanding of this powerful force.
At spaceyv.com, we continue to explore the wonders of the cosmos, from mysterious forces like the Great Attractor to the possibility of extraterrestrial life. As telescopes and observational technology improve, we may one day unlock even more secrets about the forces shaping our universe. The mysteries of the cosmos are far from solved, but with each new discovery, we come one step closer to understanding our place in this vast and ever-expanding universe.
What do you think?
Do you believe that dark matter and hidden galaxy clusters fully explain the Great Attractor, or could there be an even greater cosmic mystery waiting to be uncovered? Let us know in the comments below!
References