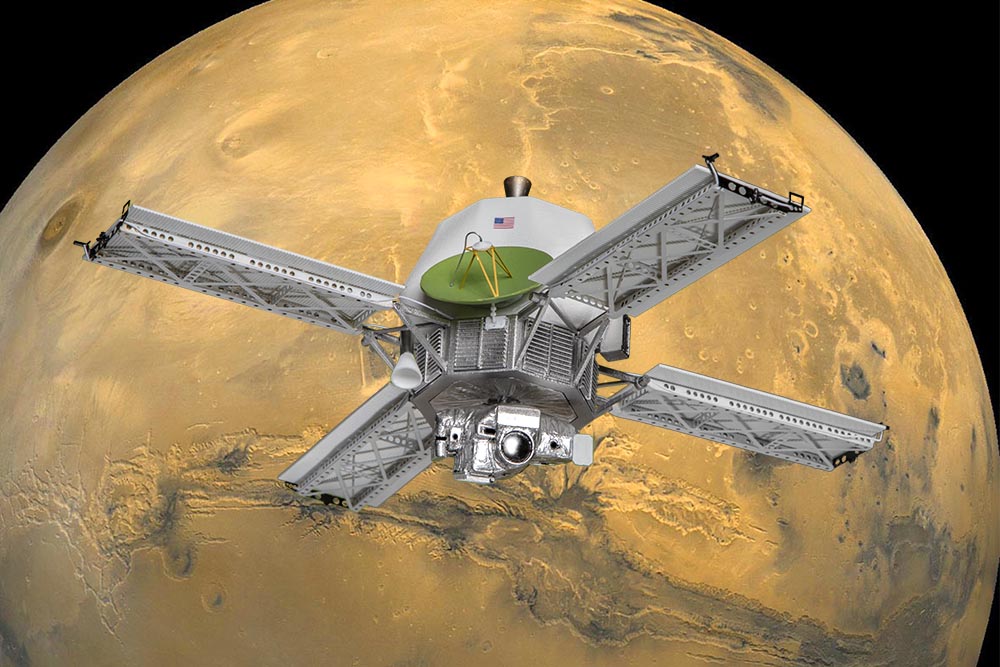
In the vast expanse of our solar system, the red planet Mars has captivated the human imagination for centuries. The year 1971 marked a significant milestone in the space exploration of Mars with the successful mission of Mariner 9, a spacecraft that revolutionized our understanding of the Martian landscape and atmosphere. read this article on Spaceyv.
Launching Towards the Red Frontier
Launch Date and Objectives:
- On May 30, 1971, NASA’s Mariner 9 embarked on a journey to Mars, setting out to conduct an extensive study of the planet’s surface, atmosphere, and climate.
- Mariner 9 was the first spacecraft designed to orbit another planet, heralding a new era in planetary exploration.
Arrival at the Red Planet
Orbital Insertion:
- After a five-month journey, Mariner 9 arrived at Mars on November 14, 1971, and executed a successful orbital insertion, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit another planet in our solar system.
Global Dust Storm:
- However, upon arrival, Mariner 9 encountered an unexpected challenge – a global dust storm had engulfed the entire planet, obscuring the Martian surface. This prompted the mission team to patiently wait for the storm to subside.
Unveiling the Martian Landscape – Mariner 9
Revelation of Valles Marineris:
- As the dust settled, Mariner 9 revealed the breathtaking Martian landscape, including the discovery of Valles Marineris, a vast canyon system stretching across the equator of Mars. This geological marvel was named in honor of the spacecraft.
Volcanoes and Ice Caps:
- Mariner 9’s instruments captured images of towering volcanoes, such as Olympus Mons, the largest volcano in the solar system, and polar ice caps, providing valuable insights into the Martian climate and seasonal changes.
Pioneering Martian Weather Studies
Atmospheric Investigations:
- Mariner 9 conducted extensive studies of Mars’ thin atmosphere, revealing details about its composition, temperature variations, and the presence of dust storms.
- The mission significantly contributed to our understanding of the Martian weather patterns.
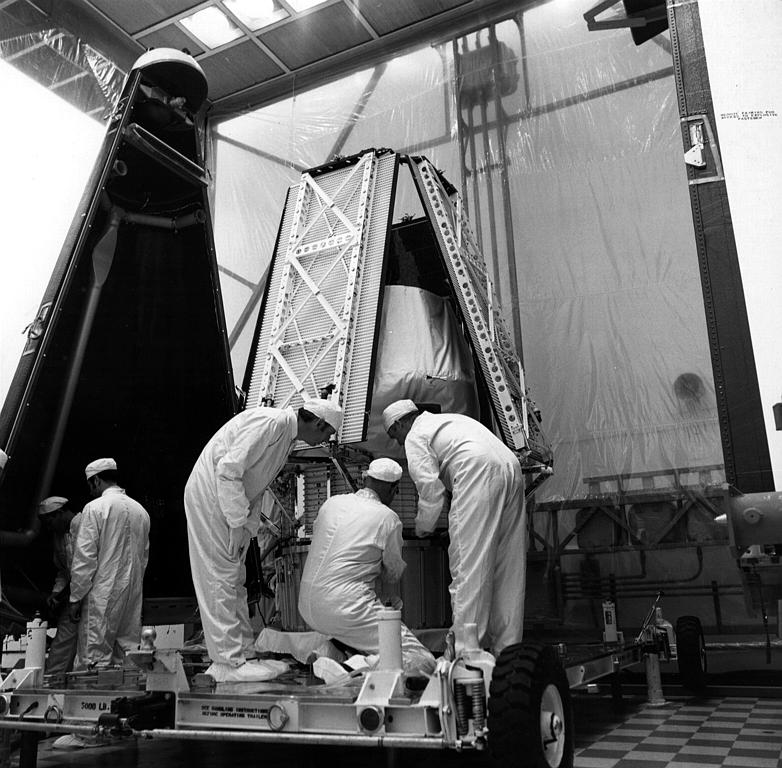

Legacy and Impact
Extended Mission:
- Originally planned for a 90-day mission, Mariner continued to function for almost a year, capturing over 7,000 images and transmitting invaluable data back to Earth.
Scientific Contributions:
- The wealth of data gathered by Mariner laid the groundwork for subsequent Mars missions, influencing the design and objectives of future spacecraft exploring the red planet.
Looking Forward
Inspiring Future Exploration:
- Mariner 9’s success paved the way for a continued interest in Mars exploration, setting the stage for ambitious missions like the Mars rovers and orbiters that followed.
Continued Fascination:
- Today, as we strive to unlock the mysteries of Mars, Mariner remains a testament to the pioneering spirit of space exploration and the enduring human curiosity that propels us to explore the cosmos.
In 1971, Mariner 9 not only became a trailblazer in planetary exploration but also ignited a fervor for understanding the mysteries of Mars, a fascination that continues to drive our quest for knowledge about the red planet and the potential for life beyond Earth. thanks for staying with spaceyv.



