Microwaves in space play a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of the universe. From mapping the cosmic microwave background radiation to studying distant galaxies, these invisible waves offer invaluable insights into the structure, composition, and evolution of the cosmos. In this article in Spaceyv, we delve into the significance of microwaves in space exploration and their myriad applications.
Understanding Microwaves in Space:
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than those of visible light but shorter than radio waves. In space, they serve as a powerful tool for astronomers to peer into regions that are otherwise obscured by dust and gas.
Unlike visible light, microwaves can penetrate these obstructions, allowing astronomers to observe objects and phenomena that would otherwise remain hidden.
– Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than radio waves.
– In space, microwaves serve as a powerful tool for astronomers due to their ability to penetrate dust and gas, enabling observations of otherwise obscured regions.
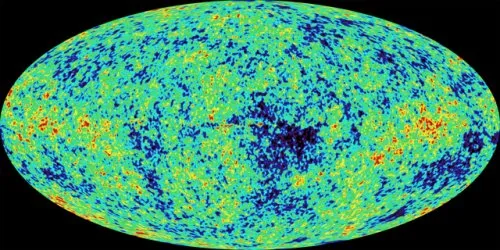
– The cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) is a key discovery in cosmology, providing insights into the early universe’s composition, age, and expansion rate.
– Microwave telescopes like the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and Planck satellite have mapped the CMB with high precision, revealing fluctuations in temperature and density that shed light on cosmic evolution.
– Microwaves also aid in studying galactic evolution by detecting emissions from dust, gas, and regions of star formation within galaxies.
– In addition, microwaves enable the study of exoplanets by detecting radio waves emitted by these distant worlds, helping astronomers infer atmospheric compositions and other characteristics.
– Advancements in technology and data analysis techniques promise even greater insights into the cosmos through microwave observations.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMB):
One of the most significant discoveries in cosmology was the detection of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). This faint glow permeates the entire universe and is a remnant of the Big Bang. Approximately 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe had cooled enough for atoms to form, leading to the release of photons.
These photons have been traveling across the cosmos ever since, gradually cooling to become the microwave background radiation we observe today. By studying the CMB, scientists can glean vital information about the early universe, including its age, composition, and rate of expansion.

Mapping the Universe
Microwave telescopes, such as the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and the Planck satellite, have been instrumental in mapping the cosmic microwave background with unprecedented precision.
These maps reveal subtle fluctuations in temperature and density, providing clues about the distribution of matter and the formation of large-scale structures in the universe. By analyzing these maps, astronomers can refine our understanding of cosmological models and the evolution of the cosmos.
Studying Galactic Evolution
Microwaves also offer insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies. Dust and gas within galaxies emit microwave radiation, which astronomers can detect using specialized instruments.
By studying this emission, scientists can infer the presence of interstellar dust, molecular clouds, and regions of active star formation. Additionally, microwaves allow astronomers to probe the cosmic microwave background for evidence of primordial gravitational waves, which could provide further support for inflationary theory.
Exploring Exoplanets
Microwaves are not only valuable for studying the distant universe but also for exploring nearby planetary systems. Instruments like radio telescopes equipped with microwave receivers can detect radio waves emitted by exoplanets.
By analyzing these signals, astronomers can infer the presence of atmospheres, magnetic fields, and other characteristics of exoplanets. This information is crucial for identifying potentially habitable worlds and understanding the diversity of planetary systems beyond our solar system.
Suggested Contents:
Galaxy, Universe & Solar Systems
Future Prospects
As technology advances, so too will our ability to harness microwaves for space exploration. Future missions may incorporate even more sensitive instruments capable of detecting fainter signals from the depths of the cosmos. Additionally, advancements in data analysis techniques will enable scientists to extract more detailed information from microwave observations, further advancing our understanding of the universe.
FAQs about Microwaves in Space
1. What are microwaves in space?
- Microwaves in space refer to a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than those of visible light but shorter than radio waves. They play a crucial role in space exploration, offering insights into various cosmic phenomena.
2. How do microwaves help astronomers study the universe?
- Microwaves can penetrate dust and gas in space, allowing astronomers to observe objects and phenomena that would otherwise remain hidden. They are particularly useful for studying the cosmic microwave background radiation, mapping galaxies, and exploring exoplanetary systems.
3. What is the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB)?
- The CMB is a faint glow that permeates the entire universe and is a remnant of the Big Bang. It provides crucial information about the early universe, including its age, composition, and rate of expansion.
4. What instruments are used to study microwaves in space?
- Instruments like microwave telescopes, such as the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and the Planck satellite, are used to study microwaves in space. These telescopes can map the cosmic microwave background radiation and detect emissions from galaxies and exoplanetary systems.
5. How do microwaves contribute to our understanding of galactic evolution?
- Microwaves allow astronomers to detect emissions from dust, gas, and regions of star formation within galaxies. By studying these emissions, scientists can gain insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies over cosmic time.
6. Can microwaves be used to study exoplanets?
- Yes, microwaves can be used to study exoplanets by detecting radio waves emitted by these distant worlds. Analyzing these signals can provide information about exoplanetary atmospheres, magnetic fields, and other characteristics.
7. What are some future prospects for using microwaves in space exploration?
- Future missions may incorporate even more sensitive instruments capable of detecting fainter signals from the cosmos. Advancements in data analysis techniques will also enable scientists to extract more detailed information from microwave observations, further advancing our understanding of the universe.
Conclusion
Microwaves in space are indispensable tools for astronomers, providing a window into the universe’s past, present, and future. From studying the cosmic microwave background to probing distant galaxies and exoplanetary systems, these invisible waves offer a wealth of information about the cosmos. As our knowledge and technology continue to evolve, microwaves will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of space exploration, helping us unlock the mysteries of the cosmos. thanks for staying with Spaceyv.