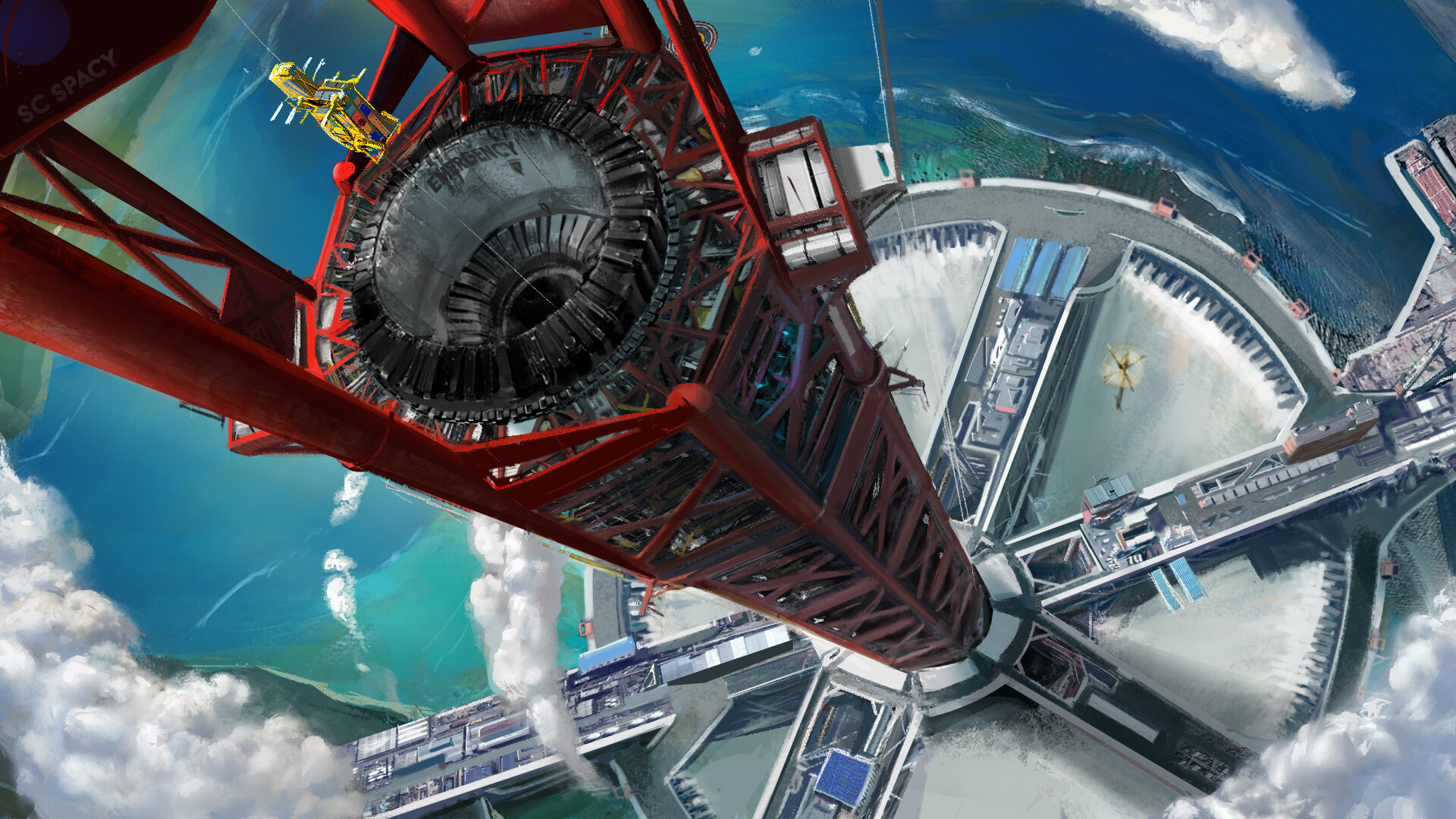
For centuries, humans have dreamed of reaching the stars with Space Elevator . From the first rockets to ambitious missions to Mars, space travel has always been a costly and energy-intensive endeavor. But what if there were a way to reach space without rockets? What if we could simply take an elevator ride into orbit?
This is the idea behind the space elevator—a revolutionary concept that could change how we explore and utilize space. But is it actually possible? Or is it just a far-fetched sci-fi fantasy? In this article, Spaceyv.com explores the challenges and possibilities of building a space elevator. Stay with Spaceyv
What Is a Space Elevator?
A space elevator is a proposed structure that would extend from Earth’s surface all the way to geostationary orbit (about 35,786 km or 22,236 miles above the planet). The concept was first introduced in 1895 by Russian scientist Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, inspired by the Eiffel Tower. Later, in the 20th and 21st centuries, scientists and engineers refined the idea with more realistic designs.
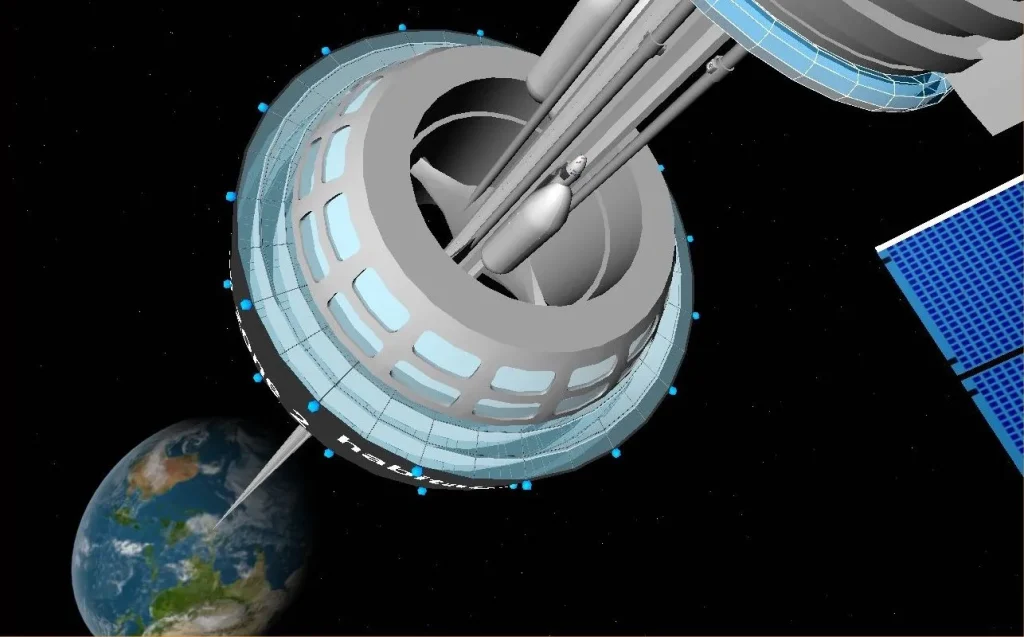
How Would It Work?
The space elevator consists of several key components:
- Anchor Station on Earth: A stable base, possibly located at the equator, where the elevator begins.
- Tether or Cable: A super-strong cable stretching from Earth to space, held in tension by Earth’s gravity pulling downward and centrifugal force pulling outward.
- Counterweight in Space: A large mass at the end of the cable (beyond geostationary orbit) that keeps the tether taut.
- Climber Vehicles: Robotic elevators that would transport cargo and possibly passengers up and down the tether using electric or magnetic propulsion.
If built, a space elevator would make space travel vastly more affordable and accessible. Instead of launching expensive rockets, we could simply “ride” into orbit using solar-powered or laser-powered climbers.
The Benefits of a Space Elevator
A space elevator offers multiple advantages over traditional space travel:
1. Lower Costs
One of the biggest barriers to space exploration is cost. Current rockets require massive amounts of fuel and can cost upwards of $10,000 per kilogram to launch into orbit. A space elevator, once constructed, could reduce this cost to just a few hundred dollars per kilogram.
2. Continuous Access to Space
Unlike rockets, which require months or years of planning for each launch, a space elevator would provide a continuous and reusable way to access space, operating much like a train or highway system.
3. Environmental Benefits
Rockets produce large amounts of carbon emissions and can damage the ozone layer. A space elevator would be powered by clean energy, reducing the environmental impact of space travel.
4. Larger Payloads
With a space elevator, we could transport larger and heavier loads into space without worrying about rocket size limitations. This could revolutionize satellite deployment, space station construction, and even future space colonization efforts.
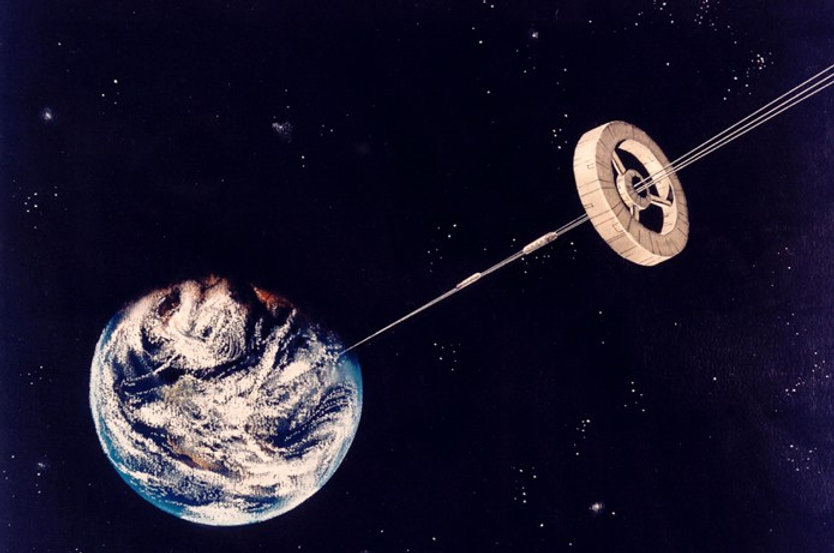
The Challenges of Building a Space Elevator
While the benefits of a space elevator are undeniable, there are also significant engineering, financial, and scientific challenges that must be overcome.
1. The Cable: Stronger Than Anything We’ve Ever Built
The biggest challenge is finding a material strong enough to support a 35,000+ km-long tether under constant tension. Current materials like steel or Kevlar are far too weak.
Possible Materials:
- Carbon Nanotubes: Some of the strongest materials known, but we currently lack the ability to produce them at the necessary scale.
- Graphene: Another promising material, but like carbon nanotubes, large-scale production is a challenge.
- Diamond Nanothreads: A new and promising material, but still in early research stages.
2. Avoiding Space Debris and Meteorites
A cable extending into space would be at risk of collisions with satellites, space debris, and meteorites. Scientists would need to develop tracking systems and possibly shielding mechanisms to prevent catastrophic failures.
3. Stabilization and Weather Conditions
On Earth, hurricanes, earthquakes, and strong winds could make it difficult to keep the base station stable. Engineers would need to design flexible structures that can withstand extreme weather.
4. Political and Economic Hurdles
Building a space elevator would require international cooperation, as no single country could realistically fund and operate such a massive project alone. Governments and private companies would need to work together to make it a reality.
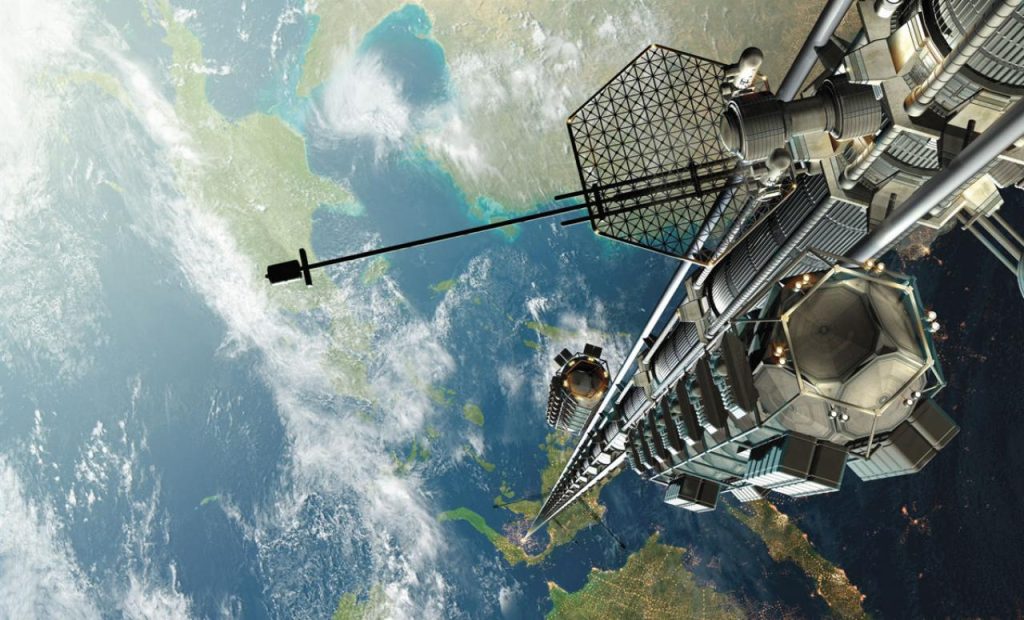

Could We Build a Space Elevator on the Moon or Mars First?
Instead of building a space elevator on Earth, some scientists have proposed constructing one on the Moon or Mars first.
Why the Moon?
- The Moon has only 1/6th of Earth’s gravity, making it easier to build a functioning space elevator.
- No atmosphere means no weather-related challenges like storms or strong winds.
- It could serve as a stepping stone for Mars missions and deep-space exploration.
Why Mars?
- Mars has lower gravity than Earth, reducing the stress on the tether.
- It could be a key part of future Mars colonization efforts.
If successful, a Lunar or Martian space elevator could provide valuable insights before attempting one on Earth.
When Could a Space Elevator Become Reality?
Given the current technological challenges, experts estimate that we are still several decades away from building a working space elevator. However, advancements in nanotechnology, material science, and robotics are bringing us closer.
- NASA and private companies like Obayashi Corporation (a Japanese construction company) have proposed building a space elevator by 2050.
- The International Space Elevator Consortium (ISEC) is actively researching solutions for building a functioning space elevator.
- Ongoing developments in graphene production and nanotechnology could make strong-enough materials available sooner than expected.
With continued innovation and investment, a space elevator could transition from science fiction to science fact within the next century.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Space Travel
The idea of a space elevator represents one of the most ambitious engineering projects in human history. While challenges remain, the potential benefits—cheaper space travel, continuous access to orbit, and a sustainable pathway to the stars—make it an exciting possibility worth pursuing.
At Spaceyv.com, we remain dedicated to exploring the latest developments in space exploration and technology. The dream of a space elevator may be closer than we think, and the journey to making it a reality is just beginning.
What Do You Think?
Do you believe a space elevator will ever be built? What challenges do you think are the hardest to overcome? Let us know in the comments!



