The Big Bang Theory stands as one of the most captivating and profound concepts in modern astronomy. It not only explains the origins of the universe but also provides a framework for understanding its evolution.
Delving into the depths of cosmic history, the Big Bang Theory unveils a narrative of cosmic expansion, the formation of galaxies, and the birth of fundamental elements. In this exploration, we uncover the essence of this astronomical enigma, shedding light on its significance and the profound insights it offers into our universe’s past, present, and future. stay with Spaceyv
What is the Big Bang Theory?
According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe started as a very hot, dense state about 13.8 billion years ago. A singularity is an infinitely small point that was compressed into existence at the beginning of the universe, containing all matter, energy, space, and time. The universe then burst into a massive explosion that marked the beginning of its rapid expansion and created the vast cosmos that we see today.
| Stage | Time After Big Bang | Event Name | What Happened | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 seconds | Singularity | Universe began from an infinitely hot, dense point. | Space, time, and energy were born. |
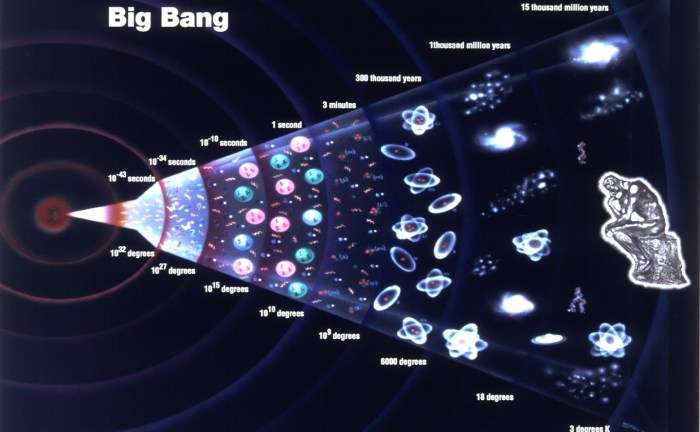
| 2 | 10⁻³⁶ to 10⁻³² seconds | Inflation | Universe expanded exponentially faster than the speed of light. | Smoothed out the universe and set the stage for structure. |
| 3 | 10⁻¹² to 10⁻⁶ seconds | Quark Epoch | Quarks and gluons appeared. Matter and antimatter began forming. | Ingredients for protons and neutrons emerged. |
| 4 | ~1 second | Hadron Epoch | Quarks combined into hadrons (protons & neutrons). Neutrinos decoupled. | Matter slightly outnumbered antimatter. |
| 5 | 3 minutes | Nucleosynthesis | Formation of light atomic nuclei like hydrogen, helium, and lithium. | Universe now contains basic building blocks of matter. |
| 6 | 380,000 years | Recombination | Electrons combined with nuclei to form neutral atoms. | Universe became transparent, and light (CMB) was released. |
| 7 | 300 million years and beyond | Structure Formation | Gas clouds collapsed into stars and galaxies. Universe continued expanding. | Galaxies, stars, and eventually planets like Earth formed. |
-
The Big Bang isn’t just one event—it’s a timeline of transformations.
-
It describes how the universe expanded, cooled, and evolved from a quantum speck into everything we see today.
-
We’re currently in the 7th stage: stars and galaxies are still forming and the universe continues to expand.
Evidence of the big bang theory
Even though the Big Bang theory may appear speculative, astronomers have gathered strong evidence to support it. The cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), a faint glow that permeates the universe, is one important piece of evidence. The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) was founded in 1965 and is regarded as a remnant of the Big Bang, offering a glimpse into the early stages of the universe when it changed from hot plasma to transparent gas.
Additionally, the abundance of light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, aligns with predictions made by the Big Bang Theory. These elements, forged in the fiery furnaces of the early universe, serve as cosmic fingerprints, affirming the narrative of cosmic evolution.
Who proposed the Big Bang theory?
The Big Bang Theory was proposed by the Belgian physicist and Catholic priest Georges Lemaître in 1927.
According to Lemaître’s theory, the “Cosmic Egg” or “Primeval Atom” is the hypothetical first atom from which the universe originated. According to his theory, this primordial atom bursts, causing the universe to expand and eventually give rise to galaxies and other cosmic structures. Though initially viewed with skepticism, Lemaître’s theories gained traction as the idea of an expanding universe was supported by an increasing amount of observational data, ultimately leading to the development of the Big Bang Theory as we know it today.
Related Contents:
Where do Black Holes Take You?
Galaxy, Universe & Solar Systems

🌌 The 7 Stages of the Big Bang Theory
Brought to you by spaceyv — Exploring the Universe, One Star at a Time
1. The Singularity (Time = 0)
At the very beginning, the entire universe was compressed into an unimaginably hot, dense point—called a singularity.
-
No space, no time, no matter—just pure energy in a single point.
-
This is the moment before the Big Bang.
🧠 Imagine the universe fitting into something smaller than an atom!
2. Inflation (10⁻³⁶ to 10⁻³² seconds)
Suddenly, this singularity exploded outward (not into space, but creating space itself) in a process called cosmic inflation.
-
The universe expanded faster than the speed of light.
-
Quantum fluctuations were stretched across space, seeding the future galaxies.
📈 The universe grew from subatomic size to something grapefruit-sized in a fraction of a second.
3. The Quark Epoch (10⁻¹² seconds to 10⁻⁶ seconds)
As things cooled slightly, particles began to form—starting with quarks and gluons.
-
Too hot for atoms to exist yet.
-
Energy and matter were essentially the same thing.
💥 The building blocks of protons and neutrons were born here.
4. The Hadron Epoch (up to 1 second)
Quarks began binding into hadrons (like protons and neutrons).
-
Antimatter and matter were annihilating each other, but slightly more matter remained.
-
Neutrinos were set free—still traveling through space today.
⚛️ This stage helped shape the structure of atomic nuclei.
5. Nucleosynthesis (3 minutes)
Three minutes after the Big Bang, the universe had cooled enough for protons and neutrons to combine into nuclei.
-
Mostly hydrogen and helium nuclei formed (with a touch of lithium).
-
Still no atoms—just nuclei and free electrons.
🔥 This era set the stage for the elements we know today.
6. Recombination & Photon Release (380,000 years later)
Electrons finally slowed down enough to combine with nuclei → atoms were born.
-
This created neutral hydrogen and helium atoms.
-
Light could now travel freely: this is the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR).
📷 We can still detect this “afterglow” of the Big Bang today.
7. Galaxy Formation & Structure (300 million years and beyond)
Gravity pulled together gas clouds to form the first stars, galaxies, and black holes.
-
This era continues today with galaxies evolving, merging, and creating new stars.
-
Dark matter and dark energy also shape the universe’s fate.
🌌 We’re now 13.8 billion years into this stage—right here on Earth, inside a galaxy called the Milky Way.
🔭 Recap: The 7 Stages of the Big Bang Theory
| Stage | Name | What Happened |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singularity | Time, space, energy begin |
| 2 | Inflation | Rapid exponential expansion |
| 3 | Quark Epoch | Subatomic particles form |
| 4 | Hadron Epoch | Protons and neutrons appear |
| 5 | Nucleosynthesis | Light elements created |
| 6 | Recombination | Atoms form; light escapes (CMB) |
| 7 | Structure Formation | Stars, galaxies, planets evolve |
🧠 Bonus Insight from spaceyv
The Big Bang wasn’t an explosion in space—it was an expansion of space. Time, space, and the laws of physics were born with it.
And the most mind-blowing part? The universe is still expanding, possibly forever.



